US Financial Investment Analysis
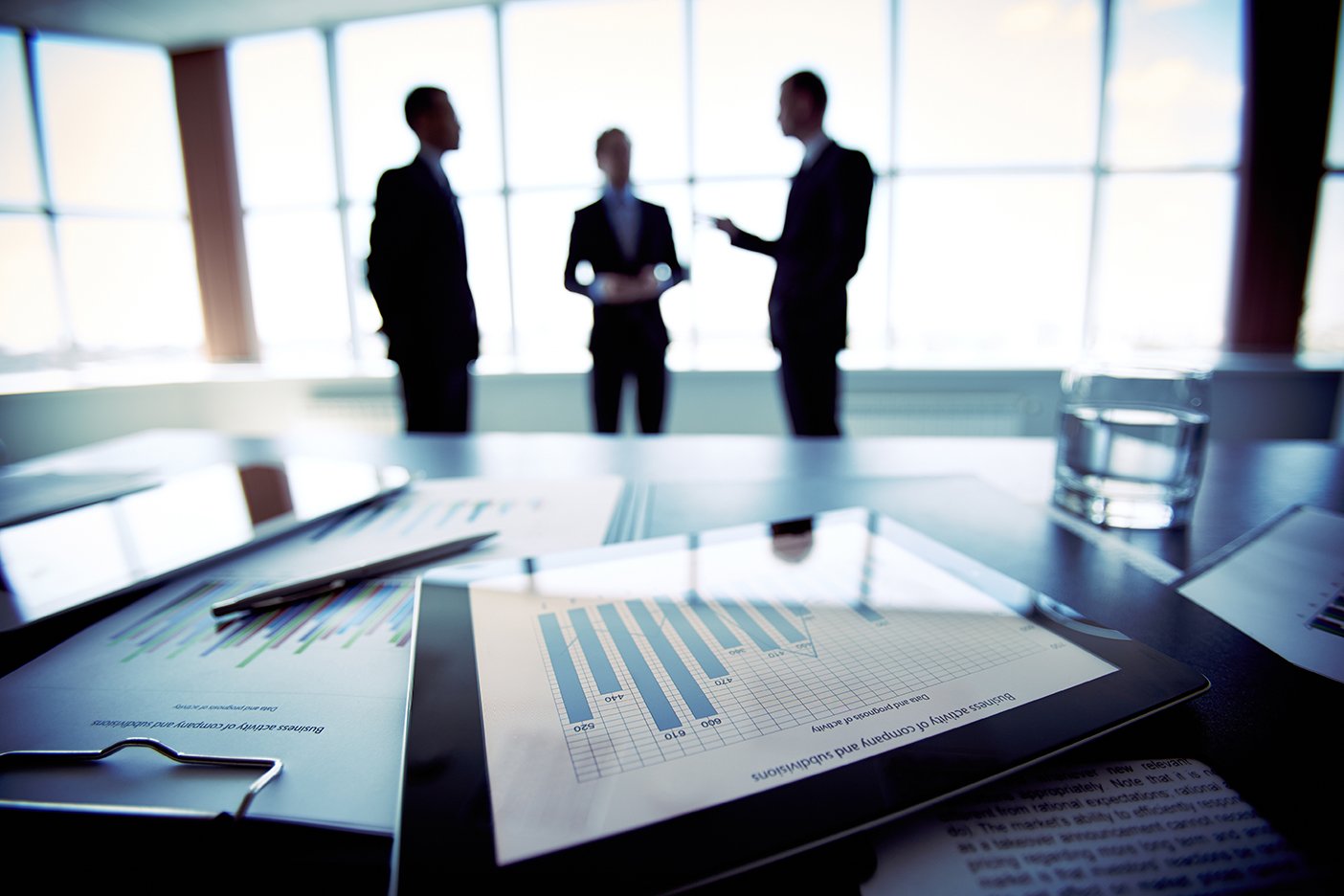
Financial investment in the United States plays a crucial role in shaping the economy, providing opportunities for individuals and institutions to grow wealth and achieve financial goals. As one of the world's largest and most dynamic markets, understanding the various aspects of US financial investment is essential for both novice and experienced investors.
Financial Market Overview
The US financial markets encompass a wide range of investment options, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real estate. The stock market, primarily represented by indices such as the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average, allows investors to purchase shares in publicly traded companies. This equity investment offers the potential for high returns but also comes with higher risk due to market volatility.
On the other hand, bonds are generally considered safer investments. When investors purchase bonds, they are essentially lending money to governments or corporations in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of principal at maturity. Bonds can provide stability to a portfolio, especially during uncertain economic times.
Investment Strategies
Successful investing requires thoughtful strategies. Some common approaches include:
-
Value Investing: This strategy focuses on identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals. Investors look for companies trading below their intrinsic value, expecting the market to eventually recognize their worth.
-
Growth Investing: Growth investors seek companies with above-average growth rates compared to industry peers. This approach often involves investing in technology or biotech companies where innovation drives rapid expansion.
-
Income Investing: This strategy revolves around generating steady income streams, typically through dividend-paying stocks or bonds. Income investors prioritize cash flow, making this approach attractive to retirees or those seeking passive income.
-
Index Investing: Rather than selecting individual stocks, index investors purchase portfolios that mirror market indices. This passive strategy aims to achieve market returns while minimizing costs and risks associated with active management.
Risks and Considerations
All investments carry risks, and understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions. Market volatility, economic downturns, and interest rate changes can significantly impact investment performance. Diversification—spreading investments across various asset classes—can help mitigate risk by reducing exposure to any single investment.
Additionally, investors should consider their risk tolerance, investment timeline, and financial goals. Younger investors may be more willing to take risks for higher returns, while those approaching retirement might prefer safer, income-generating investments.
The Role of Financial Advisors
For many individuals, navigating the complexities of financial investment can be daunting. Financial advisors can provide personalized guidance, helping clients develop tailored investment strategies based on their unique circumstances. Advisors can also assist with portfolio management and asset allocation, ensuring investments align with overall financial objectives.
Conclusion
Investing in US financial markets offers significant opportunities for wealth creation but requires a thorough understanding of various investment instruments and strategies. By assessing personal goals, embracing diversification, and potentially seeking professional advice, investors can navigate market complexities and work toward achieving their financial aspirations. As the economic landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable remains essential for successful investing.